Industrial Pump Maintenance: Why It’s Critical for Reliable Facility Operations
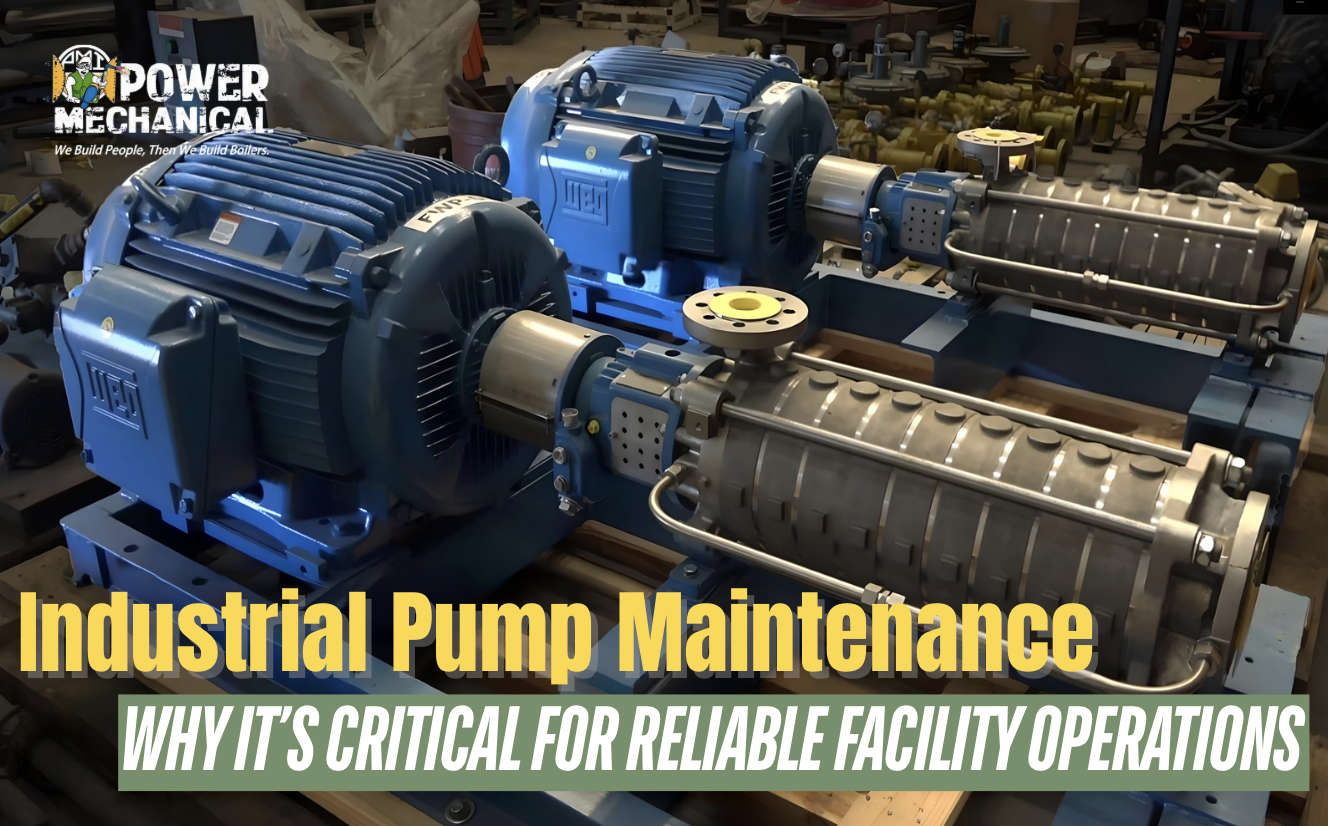

Industrial & Commercial Facilities rely on various pumps for various operations around a steam boiler room. From boiler feedwater and condensate return to chilled water circulation, and fuel oil transfer. Pumps are the backbone of mechanical rooms across many industries. For example, hospitals, schools, manufacturing facilities, and food production plants depend on continuous steam and hot water within their buildings.
Because these components are so critical, regular pump maintenance and monitoring are essential. As a result, facilities can prevent unexpected downtime, costly repairs, and system failures. According to the Hydraulic Institute, proper pump operation and maintenance are essential for long-term reliability and system efficiency.
The Critical Role Pumps Play in Mechanical Rooms
Most facilities are home to multiple pumps, each serving a specific purpose, including:
-
Boiler feedwater circulation
-
Condensate return systems
-
Chilled water and cooling loops
-
Fuel oil delivery
-
Fire protection and suppression systems
As a result, a single pump failure can disrupt operations, reduce efficiency, and impact safety. This is why pumps should always be included in a structured preventive maintenance program.
Cavitation: One of the Leading Causes of Pump Failure
Within boiler and condensate systems, cavitation is one of the most common causes of pump damage.
Cavitation occurs when liquid at the suction side of a pump drops below its vapor pressure and begins to form vapor bubbles. As these bubbles collapse inside the impeller, they create a shock-like effect that can:
-
Erode impellers and internal components
-
Reduce pump efficiency
-
Cause vibration, noise, and eventual failure
🔊 Common warning sign: a sound similar to sand, rocks, or marbles rattling inside the pump casing.
While cavitation cannot always be prevented through maintenance alone, monitoring temperature, pressure, and suction conditions can help identify a developing issue before serious damage occurs.


Boiler Feedwater Pumps: Selection and Monitoring Matter
Boiler feedwater pumps must handle high-temperature condensate while overcoming the boiler’s operating pressure. These pumps are selected based on a defined performance curve and should only be replaced with equipment that meets those same performance requirements.
Pumps operating too far left or right on their performance curve are far more likely to fail.
Best practices include:
-
Installing and maintaining suction and discharge pressure gauges
-
Ensuring Net Positive Suction Head Available (NPSHa) exceeds NPSH Required (NPSHr)
-
Monitoring operating conditions regularly to reduce cavitation risk
Developing an Effective Pump Maintenance Plan
Industrial pumps typically require minimal hands-on maintenance, but neglect can quickly lead to failure. An effective maintenance plan starts with identifying all critical system pumps throughout the facility.
Key maintenance practices include:
-
Following manufacturer-recommended service intervals
-
Proper bearing lubrication
-
Monitoring bearing temperature
-
Checking vibration and alignment
Misalignment and excessive vibration are two of the fastest ways to damage a pump. Larger facilities often install vibration sensors to remotely monitor conditions and alert operators to changes before a failure occurs.

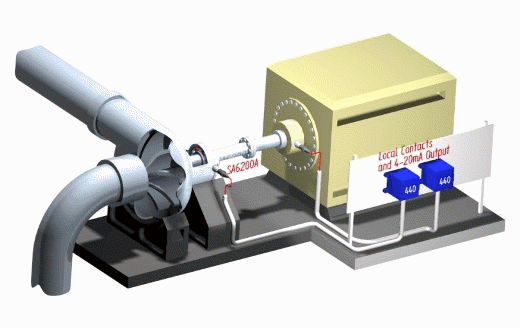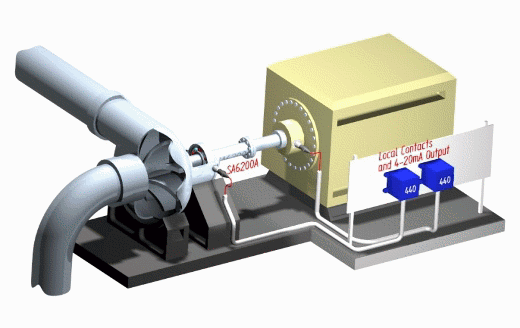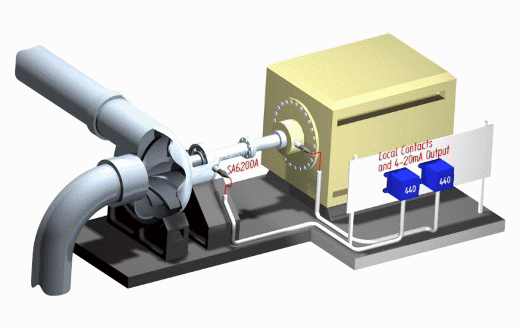
Vibration, Couplings, and Seals: Early Warning Signs
An increase in vibration is often the first indication that something has changed within a pump system, making routine monitoring extremely valuable.
Maintenance teams should:
-
Inspect couplings at least annually
-
Look for worn, cracked, or damaged components
-
Replace couplings proactively rather than after failure
Planned coupling replacement is far more cost-effective than dealing with an unexpected pump outage.
Leaks are another key warning sign. In normal operation, the only place a pump should be wet is inside its casing. External leaks often indicate:
-
Worn shaft seals
-
Insufficient packing
-
Seal misalignment
Routine inspection allows seals to be replaced before they cause system downtime.


Preventing Pump Failure Through Regular Monitoring
Ultimately, consistent monitoring is the most effective way to extend pump life and reduce unexpected failures.
-
Pressure readings
-
Lubrication condition
-
Vibration levels
-
Visible leaks
This allows issues to be identified early and addressed quickly — often preventing full pump repair or replacement.


Pump Repair, Replacement, and Refurbishment Support
If your facility requires pump repair, replacement, or refurbishment, Power Mechanical, Inc. offers a dedicated pump repair and valve shop designed to return critical systems to service quickly and cost-effectively.
📞 Call: 1-877-764-7832
🌐 Visit: powermechanical.com